题目描述
给你一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后链表的头节点。你必须在不修改节点内部的值的情况下完成本题(即,只能进行节点交换)。
示例 1:
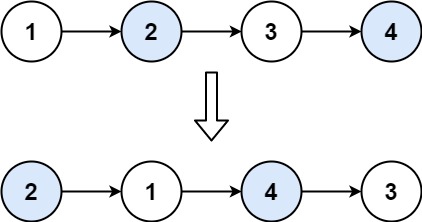
输入:head = [1,2,3,4]
输出:[2,1,4,3]
示例 2:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:head = [1]
输出:[1]
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目在范围 [0, 100] 内
- 0 <= Node.val <= 100
解决方法
C++
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy->next = head;
ListNode* current = dummy;
while (current->next && current->next->next) {
ListNode* node1 = current->next;
ListNode* node2 = current->next->next;
current->next = node2;
node1->next = node2->next;
node2->next = node1;
current = node1;
}
return dummy->next;
}
};
|
结果
执行用时 : 0 ms, 击败 100.00% 使用 C++ 的用户
内存消耗 : 9.32 MB, 击败 5.03% 使用 C++ 的用户
Java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
public class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode current = dummy;
while (current.next != null && current.next.next != null) {
ListNode node1 = current.next;
ListNode node2 = current.next.next;
current.next = node2;
node1.next = node2.next;
node2.next = node1;
current = node1;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
|
结果
执行用时 : 0 ms, 击败 100.00% 使用 Java 的用户
内存消耗 : 40.38 MB, 击败 5.18% 使用 Java 的用户
Python
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
class Solution(object):
def swapPairs(self, head):
dummy = ListNode(0)
dummy.next = head
current = dummy
while current.next and current.next.next:
node1 = current.next
node2 = current.next.next
current.next = node2
node1.next = node2.next
node2.next = node1
current = node1
return dummy.next
|
结果
执行用时 : 14 ms, 击败 75.45% 使用 Python 的用户
内存消耗 : 11.44 MB, 击败 97.48% 使用 Python 的用户
Python3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
dummy = ListNode(0)
dummy.next = head
current = dummy
while current.next and current.next.next:
node1 = current.next
node2 = current.next.next
current.next = node2
node1.next = node2.next
node2.next = node1
current = node1
return dummy.next
|
结果
执行用时 : 33 ms, 击败 90.27% 使用 Python3 的用户
内存消耗 : 16.45 MB, 击败 30.15% 使用 Python3 的用户
C
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
struct ListNode* swapPairs(struct ListNode* head) {
struct ListNode* dummy = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
dummy->next = head;
struct ListNode* current = dummy;
while (current->next && current->next->next) {
struct ListNode* node1 = current->next;
struct ListNode* node2 = current->next->next;
current->next = node2;
node1->next = node2->next;
node2->next = node1;
current = node1;
}
return dummy->next;
}
|
结果
执行用时 : 0 ms, 击败 100.00% 使用 C 的用户
内存消耗 : 5.71 MB, 击败 95.91% 使用 C 的用户
C#
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
public class Solution {
public ListNode SwapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode current = dummy;
while (current.next != null && current.next.next != null) {
ListNode node1 = current.next;
ListNode node2 = current.next.next;
current.next = node2;
node1.next = node2.next;
node2.next = node1;
current = node1;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
|
结果
执行用时 : 57 ms, 击败 88.57% 使用 C# 的用户
内存消耗 : 39.66 MB, 击败 5.71% 使用 C# 的用户
JavaScript
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
var swapPairs = function(head) {
let dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
let current = dummy;
while (current.next && current.next.next) {
let node1 = current.next;
let node2 = current.next.next;
current.next = node2;
node1.next = node2.next;
node2.next = node1;
current = node1;
}
return dummy.next;
};
|
结果
执行用时 : 37 ms, 击败 100.00% 使用 JavaScript 的用户
内存消耗 : 49.33 MB, 击败 5.29% 使用 JavaScript 的用户
TypeScript
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
function swapPairs(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
let dummy: ListNode = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
let current: ListNode | null = dummy;
while (current?.next && current?.next?.next) {
let node1: ListNode | null = current.next;
let node2: ListNode | null = current.next.next;
if (node1 && node2) {
current.next = node2;
node1.next = node2.next;
node2.next = node1;
current = node1;
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
|
结果
执行用时 : 60 ms, 击败 86.10% 使用 TypeScript 的用户
内存消耗 : 51.79 MB, 击败 5.02% 使用 TypeScript 的用户
PHP
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
class Solution {
function swapPairs($head) {
$dummy = new ListNode(0);
$dummy->next = $head;
$current = $dummy;
while ($current->next && $current->next->next) {
$node1 = $current->next;
$node2 = $current->next->next;
$current->next = $node2;
$node1->next = $node2->next;
$node2->next = $node1;
$current = $node1;
}
return $dummy->next;
}
}
|
结果
执行用时 : 11 ms, 击败 16.67% 使用 PHP 的用户
内存消耗 : 19.93 MB, 击败 5.55% 使用 PHP 的用户
Swift
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
class Solution {
func swapPairs(_ head: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
let dummy = ListNode(0)
dummy.next = head
var current: ListNode? = dummy
while current?.next != nil && current?.next?.next != nil {
let node1 = current?.next
let node2 = current?.next?.next
current?.next = node2
node1?.next = node2?.next
node2?.next = node1
current = node1
}
return dummy.next
}
}
|
结果
执行用时 : 0 ms, 击败 100.00% 使用 Swift 的用户
内存消耗 : 15.22 MB, 击败 20.67% 使用 Swift 的用户
Kotlin
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
class Solution {
fun swapPairs(head: ListNode?): ListNode? {
val dummy = ListNode(0)
dummy.next = head
var current: ListNode? = dummy
while (current?.next != null && current.next?.next != null) {
val node1 = current.next
val node2 = current.next?.next
current.next = node2
node1?.next = node2?.next
node2?.next = node1
current = node1
}
return dummy.next
}
}
|
结果
执行用时 : 138 ms, 击败 81.08% 使用 Kotlin 的用户
内存消耗 : 33.44 MB, 击败 32.43% 使用 Kotlin 的用户
Dart
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
Definition for singly-linked list.
class ListNode {
class Solution {
ListNode? swapPairs(ListNode? head) {
ListNode? tail = head;
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
if (tail == null) {
return head;
}
tail = tail.next;
}
ListNode? pre;
ListNode? cur = head;
while (cur != tail) {
ListNode? temp = cur?.next;
cur?.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
head?.next = swapPairs(tail);
return pre;
}
}
|
结果
执行用时 : 302 ms, 击败 22.22% 使用 Dart 的用户
内存消耗 : 147.56 MB, 击败 55.56% 使用 Dart 的用户
Go
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
func swapPairs(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
dummy := &ListNode{Val: 0, Next: head}
current := dummy
for current.Next != nil && current.Next.Next != nil {
node1 := current.Next
node2 := current.Next.Next
current.Next = node2
node1.Next = node2.Next
node2.Next = node1
current = node1
}
return dummy.Next
}
|
结果
执行用时 : 0 ms, 击败 100.00% 使用 Go 的用户
内存消耗 : 1.97 MB, 击败 26.06% 使用 Go 的用户
Ruby
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
def swap_pairs(head)
dummy = ListNode.new(0)
dummy.next = head
current = dummy
while current.next && current.next.next
node1 = current.next
node2 = current.next.next
current.next = node2
node1.next = node2.next
node2.next = node1
current = node1
end
dummy.next
end
|
结果
执行用时 : 47 ms, 击败 100.00% 使用 Ruby 的用户
内存消耗 : 206.64 MB, 击败 -% 使用 Ruby 的用户
Scala
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
object Solution {
def swapPairs(head: ListNode): ListNode = {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head
}
val t1 = head.next
val t2 = head.next.next
t1.next = head
head.next = swapPairs(t2)
t1
}
}
|
结果
执行用时 : 460 ms, 击败 85.71% 使用 Scala 的用户
内存消耗 : 56.41 MB, 击败 14.29% 使用 Scala 的用户
Rust
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
impl Solution {
pub fn swap_pairs(head: Option<Box<ListNode>>) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> {
if let Some(mut node) = head {
if let Some(mut next) = node.next.take() {
node.next = Self::swap_pairs(next.next.take());
next.next = Some(node);
Some(next)
} else {
Some(node)
}
} else {
None
}
}
}
|
结果
执行用时 : 0 ms, 击败 100.00% 使用 Rust 的用户
内存消耗 : 2.15 MB, 击败 21.54% 使用 Rust 的用户
Racket
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
(define (swap-pairs head)
(cond
((or (not head) (not (list-node? head)) (not (list-node? (list-node-next head))))
head)
(else
(let ((node1 head)
(node2 (list-node-next head))
(rest (list-node-next (list-node-next head))))
(set-list-node-next! node1 (swap-pairs rest))
(set-list-node-next! node2 node1)
node2))))
|
结果
执行用时 : 175 ms, 击败 100.00% 使用 Racket 的用户
内存消耗 : 98.80 MB, 击败 100.00% 使用 Racket 的用户
Erlang
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
-spec swap_pairs(Head :: #list_node{} | null) -> #list_node{} | null.
swap_pairs(Head) when Head =:= null -> null;
swap_pairs(Head) when is_record(Head, list_node) ->
case Head#list_node.next of
null -> Head;
Next ->
NewNext = swap_pairs(Next#list_node.next),
NewHead = Head#list_node{next = NewNext},
Next#list_node{next = NewHead}
end.
|
结果
执行用时 : 222 ms, 击败 -% 使用 Erlang 的用户
内存消耗 : 59.48 MB, 击败 -% 使用 Erlang 的用户
Elixir
暂时未解决
结果
执行用时 : ms, 击败 % 使用 Elixir 的用户
内存消耗 : MB, 击败 % 使用 Elixir 的用户
